Epigenetics and diet
September 11, 2019
Epigenetics provides the means by which the environment and our own habits influence on our genetics and predisposition for diseases. The major external factors that can influence our epigenetics are diet, sport and stress. In this article, we will focus on diet.
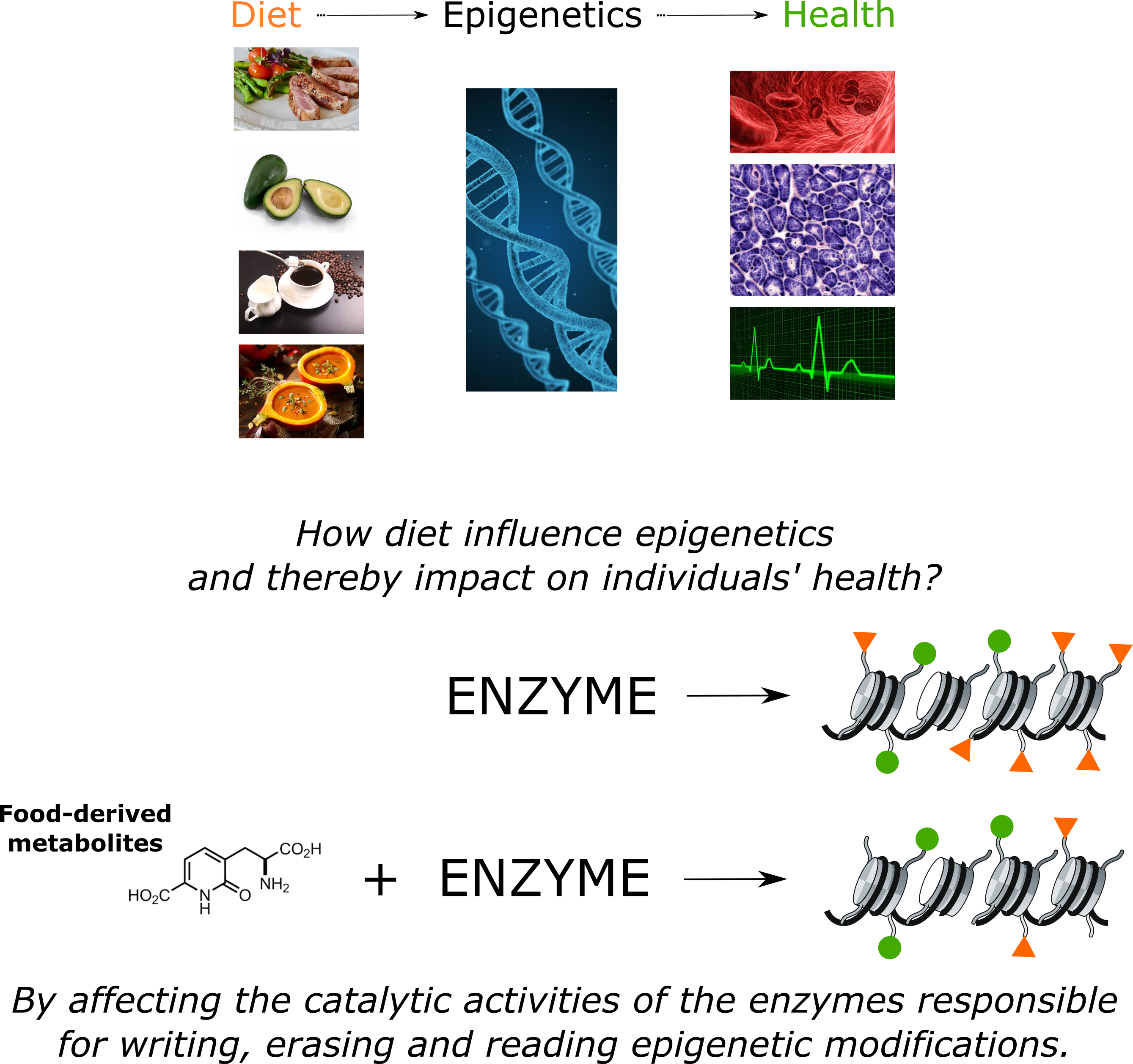
Food comsumption can exert changes in our epigenetics and thereby impact on individual health, by affecting the catalytic activities of the enzymes responsible for writing, erasing and reading epigenetic modifications.
A number of food-derived metabolites are knwon (with less or more scientific evidence) to affect DNA methylation and histone modifications.
For example, the consumption of concord grape juice has been shown to decrease depression levels in mice due to the presence
of dihydrocaffeic acid (DHCA) on this beverage. DHCA is an inhibitor of DNMT1, a writer of DNA methylation on the gene IL-6,
which when methylated increases depression levels. Another ingredient in the concord beverage is malvidin-3'-O-glucoside
(Mal-gluc), which has the effect of decreasing stress levels. Mal-gluc is an inhibitor of HDAC2, an eraser of histone H3
acetylations on the Rac1 gene. When H3 acetylation is high on this gene, stress levels decrease in mice.
Another example on how diet affects our epigenetics has been found on a common food preservative: sodium benzoate.
Sodium benzoate is metabolically converted into Benzoyl-CoA within our bodies. It has been shown that this derivative
is used by writers to increase the levels of histone benzoylation. The implications of this epigenetic modification
are still unknown.
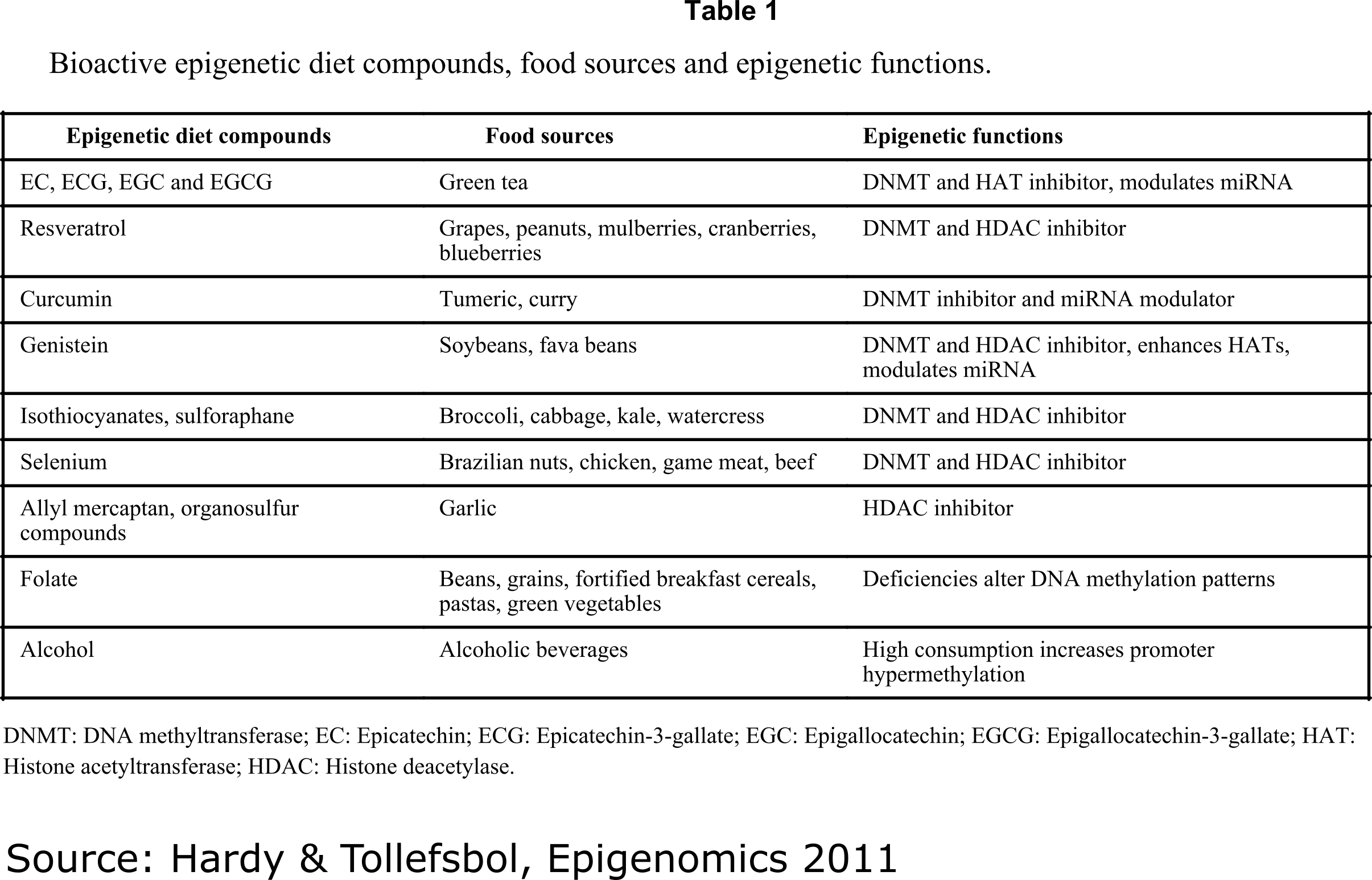
As shown in the table above, some other metabolites can induce changes in the epigenome. At EpiQMAx, we collaborate with business partners from the nutraceutical industry to assess the effect of diet and nutritional supplements on the epigenetics of individuals.